What is an Inguinal Hernia? What are the Advantages of Laparoscopy?

Definition
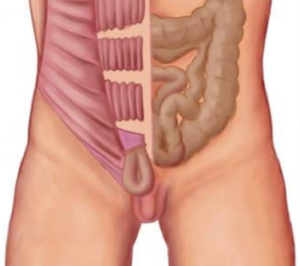
It is a common health problem that develops due to weakness in the abdominal wall structures in the groin area and results in the protrusion of intra-abdominal tissues and organs out of this weak area. This weakness is congenital (genetic) or develops later as a result of heavy lifting, coughing, sneezing and straining, which increase intra-abdominal pressure. Although it is more common in men, it is estimated to occur in 3-4 out of every 100 people. Inguinal hernia types are divided into Femoral, Direct Inguinal, Indirect Inguinal hernia and Recurrent hernias. Each of these types has different risks and treatment options. You can learn more detailed information about these from your doctor.
Symptoms
It causes symptoms such as pain, swelling or swelling in the groin area. In men, it may occur especially in the form of pain in the testicle. In fact, it can often be confused with varicocele disease. These soft and compressible swellings are more noticeable when intra-abdominal pressure increases and usually disappear when the patient lies down. However, if it is left untreated and progresses, swelling in the groin area continues even in the lying position.
What Causes Inguinal Hernia?
In men, the testicles are in the abdomen while the mother is still in the womb, and in the last two months of pregnancy, they descend to their normal position outside the body through 2 holes called the 'Inguinal Canal' in the groin area. After this descent, these 2 holes close automatically. However, in cases where this does not occur, a condition we call congenital hernia occurs. This is why inguinal hernias are more common in men than in women.
Risk factors for acquired inguinal hernias, which are more common than congenital inguinal hernias:
1- Situations that increase intra-abdominal pressure such as weight gain, heavy lifting, constipation, straining, chronic cough, urinary difficulty, pregnancy, traumas, and having a mass in the abdomen are the most common causes.
2- Excessive exercise, smoking, and prostate diseases are also risk factors.
3- Finally, diseases such as chronic lung diseases, chronic constipation and previous hernia surgery are other risk factors.
What are the risks of inguinal hernia?
With an inguinal hernia, it can reach life-threatening dimensions as a result of the internal organs protruding from this area and being squeezed out of the abdomen. As the blood flow to the trapped organ decreases or stops, gangrene and subsequent inflammation of the inner abdominal membrane and organ loss may develop. If left untreated, it will result in death. Therefore, urgent surgery is required in patients with a stuck hernia. Every minute lost brings the patient closer to more serious surgery or even death. Although the probability of this occurring is shown differently in different publications, it is realized as 5-10% annually.
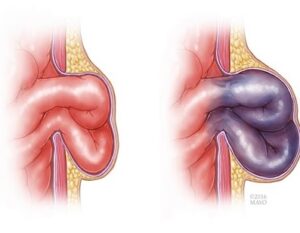
So What Should You Do If It's Not Stuck?
Inguinal hernia is a disease that needs to be treated even if it is not compressed. Mostly, patients report negativities in their family, work, social and sexual relationships due to chronic pain, and these patients are operated on as soon as possible after surgery preparations are completed. Another group postpones treatment because they do not have any active complaints or due to negativities in their family, work and social lives. In fact, these patients are the group at risk because as hernia treatment is delayed, both hernia and hernia-related problems grow and lead to worse situations. Even the size of the surgery, in its simplest form, increases over time. For this reason, we recommend surgery as soon as possible, although it is not urgent, in our patients with inguinal hernia.
Operation
The only treatment for inguinal hernia is surgery and unfortunately it is not a disease that can be cured with medication or any other method. While making the surgery plan, the physician evaluates the patient's current and previous medical condition (presence of chronic disease, surgery history, medications used and anesthesia risk) and Possible risks are discussed with the patient and the type of surgery is decided together..
What should be the type of surgery?
When current treatments for inguinal hernia are evaluated, 3 options emerge.
1- Open surgery with local anesthesia
2- Open surgery accompanied by Regional or General Anesthesia (to be decided by the anesthesiologist and the patient)
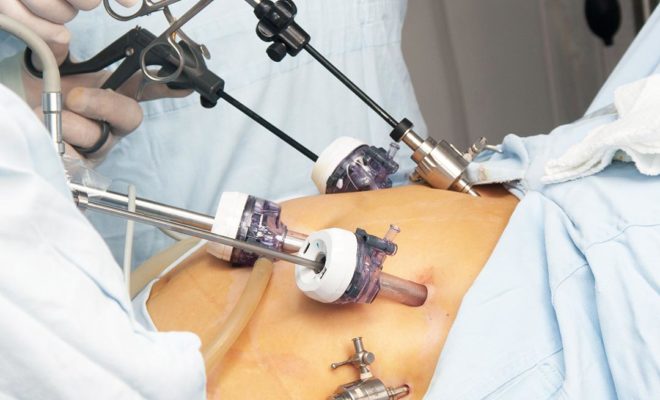
3- Laparoscopic (Endoscopic or Closed) surgery under general anesthesia
Inguinal hernia repair under local anesthesia has now been almost completely abandoned, thanks to the developments in today's anesthesia techniques. Because in this method, patients may experience serious pain and stress during and after the surgery.
Another important point is during surgery 'Patch' use of. In fact, the patch has completely changed the history of hernia repair since the day it was first invented. Today, 'Patch' has become indispensable in the world-class treatment of inguinal hernia. Many scientific studies have shown that more successful results are achieved with the use of 'Patch' in hernia repair and that the possibility of hernia recurrence is minimized. Although there are many synthetic and biological types on the market, we prefer the 'Patch' types, which are the strongest, least infection risk and most suitable at world standards, in our surgeries.
So, Open Surgery or Closed Surgery?
In open surgery, repair is performed through an approximately 5-6 cm long incision in the groin area. Closed surgery is performed with a camera and hand tools placed through 3 small holes. In both surgeries, the organs in the herniated area are taken into the abdomen and the hernia area is repaired and supported by placing a patch on it. Thus, the possibility of hernia recurrence is minimized. The procedure performed in both types of surgery is similar, but closed (Endoscopic/Laparoscopic) surgery has several advantages shown by many research and studies around the world:
1- More comfortable and less painful
2- Less wound infection
3- Less hospital stay
4- Better quality of life (especially the first 6 months)
We do not perform closed surgery on patients who are not suitable for general anesthesia, who have serious adhesions due to previous intra-abdominal surgery, and who do not want to receive general anesthesia.
Last word
All of this information is not personal opinion, but has been obtained from publications and books based on current scientific data. This article has been prepared only to provide preliminary information by reducing medical information and data to a simple form that our patients from all walks of life can understand. Therefore, it is not appropriate to make a decision on your own, based on this information, without consulting your physician. You need to meet with the relevant physician to get clear information about your condition, to clear your questions and, if necessary, to determine what your treatment will be like.
Op. Dr. Cemal Seyhun
General surgery specialist
Contact Us For Appointment:
Telephone line: 0392 444 3548 (ELIT)
Contact Form: https://www.elitenicosia.com/iletisim/